HIVI NDIVYO VITU 5 AMBAVYO PETROLEUM GEOLOGIST HUVIFANYA
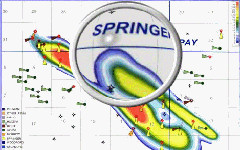
Prospecting is the work the petroleum geologist does to locate a place to drill a test hole, which hopefully can be turned into a producing oil or gas well!
Most petroleum geologists work in an office, where they have access to a lot of data.
This includes electric logs, core records, drilling records, scout
tickets, and production data. They use the data to construct maps,
cross-sections, and databases. These tools help them locate the best
places to drill their test holes.
The geologist studies his maps and cross-sections and runs computer
simulations that help him select the next best location to drill. He is
always thinking about the next drilling location…or prospect!
He will want to know what type of trap he is dealing with, and the
composition of the sedimentary rocks he will be drilling through. He
needs to estimate the porosity of his prospective “pay zone.” He wants
to know if dangerous high pressures can be expected in the new hole. If
seismic data is involved in the prospect, he will consult with the
geophysicist and get his opinion of the prospect.
The geologist is always interested in anything that happens in her
area, particularly news of new discoveries by other companies! If she
sees a promising new area, she will recommend to the land department
that an attempt be made to lease the land; the leased acreage will then
be available for drilling later.
When the geologist has finally found the correct spot, she spends much
time cross-checking to ensure she has not missed anything. She wants to
make sure she is not “surprised” by any of the following:
- Discovering the selected location was already drilled by another company 40 years ago (and was dry)
- Discovering that her company has no legal right to drill on the location (lease problems)
- Unexpected faults or other geologic problems that crop up during drilling and ruin the prospect
- Discovering that the hole is being drilled in the wrong place after
drilling begins (a very bad thing that has actually happened!)
Step 2 – The Petroleum Geologist Packages The Deal

Once the new location is defined, and the geologist is satisfied the
prospect is a good one, the work is just beginning. He has a large
amount of rough data available in the form of work maps, that he used to
satisfy himself of the feasibility. Now, he must condense this large
data mass into a set of presentation materials that can be shown to
non-geologists.
To package the deal, he will prepare sets of simplified maps and
cross-sections, highly-colored and attractive to the eye. He may use Powerpoint,
or other presentation software. Creativity, design sense, and art
skills are important during this phase. He needs to anticipate all
possible questions, and be prepared to answer each one of them. He must
be very sure of himself and his facts before he moves to the next step.
Step 3 – The Petroleum Geologist Sells the Deal

Now the geologist must step into a role that is often uncomfortable
for him … selling his prospect. It may be uncomfortable because
geologists are scientists, with scientific backgrounds and schooling.
They are used to talking to other scientists. But now the geologist must
become a salesman in order to convince people who are not geology
experts of the value of the prospect. These people may include
managers, bankers, engineers, and oil and gas investors.
Of course, the geologist wants to see her prospect drilled. But she
will take great pains to ensure all her data is presented accurately and
concisely. She is bound by her own integrity, the integrity of any
professional group she is a member of, and the integrity of her
profession.
She is looking to convince her clients that
- the prospect is worth drilling,
- investors will get a fair return for their money
- the provided financing will be money spent wisely
Even an inexpensive test hole can cost a couple of million dollars,
and some exploration tests may run into many tens of millions! So the
geologist wants to be very sure of her facts. All her clients must
believe the proposed well has a reasonable chance of being successful.
The geologist will meet with the landman (females in the business are
also called “landmen”), who will ensure the company has the legal right
to drill in the chosen spot. He will consult with the engineer, who
will determine the exact cost of drilling and completing the hole.
Marketing personnel will ensure the company has a market (buyer) for the
oil, or a pipeline for the gas. Managers, responsible for ensuring the
company’s drilling budget is spent wisely, will also approve the test.
If outside financing will be used, the geologist will explain the
prospect to representatives of the bank or other individuals or
partnerships that put up the money.
When he’s done, the geologist will have “sold” his prospect to anywhere from a few to several dozen people.
Step 4 – The Petroleum Geologist Monitors the Drilling of the Test

Next comes the part that every geologist enjoys the most! Drilling
the hole! It has now been several months since the geologist started
working on his prospect. Now the surface owners have been paid, permits
acquired, and money raised. Roads and the drilling location have been
built, pipe and supplies have been ordered. Also, the energy company
has engaged a drilling contractor who owns and operates the drilling
rig.
The drilling contractor will drill the hole in the manner specified
by the company. The contractor will have leeway to select the type of
drill bits to be used, hire a drilling crew, and make many other
decisions concerning the actual drilling. Virtually all holes are
drilled by contractors.
Drilling a hole is a very complex procedure involving many people and
many critical steps. Nearly everything must go right. Dangerous
machinery, bad weather, and continuous mechanical failures are faced
daily. The work goes on for weeks to months, 24 hours a day, nonstop. A
slip-up at any point can ruin the very expensive hole, cost a fortune,
or get people killed.
The geologist will closely monitor all aspects of the drilling as it
takes place. She will select an electric-logging company, and the proper
wireline logging tools to evaluate the hole. She will usually hire a
mud logging contractor to “sit” the well day and night. The mud logger
will study the well cuttings, report shows of oil and gas, and keep
track of other things on the location. The geologist will monitor the
formation tops as they are encountered, and discuss the progress of the
drilling with the investors. The geologist will decide where and when to
take cores or drill-stem tests. Finally, after the hole is logged with
electric logs, she will examine the logs and recommend the hole be completed or plugged.
Step 5 – The Petroleum Geologist Works With The Engineer to Complete the Well

At last the hole is drilled! At this time, a decision must quickly be made to attempt a completion and make the hole a well,
or plug the dry hole. Completion costs are extremely high, so it must
be believed the expensive completion will be worth the money. No one
wants to throw good money after bad. Justifying a completion can be a
grueling process. It almost always takes place in the middle of the
night!
The job of completing the hole is mainly in the hands of the
petroleum engineer. The engineer will decide the type of casing to use,
and the method of cementing, He will design the completion procedure
(which may involve perforating, breakdowns, acid jobs, fracks, and
pumps). However, he will depend on the geologist to advise him on
various topics. To start, the geologist will give the engineer a list of
formation tops, and tell the engineer exactly which zones should be
tested.
The geologist is often the person most familiar with the technical
practices of other oil companies in the area. No two companies are
exactly alike; some may come up with better ideas for certain
processes. The geologist may be familiar with the most successful
fracturing or breakdown procedures of other companies. He might suggest a
certain style or method of perforation, or offer advice on cementing
techniques. He will relay this information to the petroleum engineer,
who will usually be thankful for the help! Working as a team, the
geologist and petroleum engineer will get the new well completed, and put it to work providing energy for all of us!




Comments are closed.