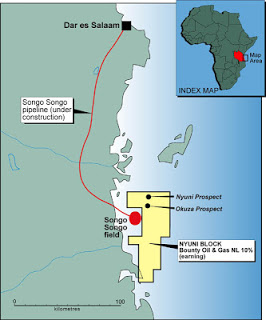
Citizens of Tanzania Support Extracting and Selling of Natural gas Internationally
A new poll from across the country shows that citizens oppose using gas as collateral for government borrowing. Released in Dar es salaam recently the study dubbed, ‘How Tanzania should use its natural gas citizens’ views from a nationwide deliberative poll’ shows more citizens support extracting and selling the country’s natural gas internationally to raise revenue, rather than directly financing domestic electricity generation.
It shows that Tanzanians nominally support ‘strict limits’ on spending gas revenue and oppose using gas as collateral for government borrowing. The study, done by Research for Poverty Alleviation (REPOA) and Center for global Development between 2014 and July 2015, also shows that most Tanzanians support both publishing all gas contracts and a role for international oversight of how the government uses gas revenues.
Most respondents also supported the idea of direct distribution of resource revenues to households in principle.But when offered a choice between cash transfers and government programmes, most Tanzanians prefer that gas revenue be spent on government programmes rather than cash transfers, according to the report. REPOA’s Executive Director Prof Chacha Wangwe said some 2,000 people from 20 districts were interviewed, including ordinary and policy makers and the findings highlighted that majority don’t want the government to borrow ahead of time.
“They want transparency. They want monies from oil and gas to largely go to education and health,”he said A stakeholder at the report’s launch, prof Ibrahim Lipumba said that the findings show that the ordinary people have an understanding of what the resource should do for the country, especially where they highlighted an importance for transparency.
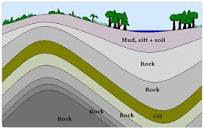
New natural resource discoveries, oil and gas provides substantial opportunity to fast-track human development progress, with updated estimates indicating that revenues to be developed could contribute between 9 per cent and 31 per cent of additional government revenues.
The tools and evidence presented are intended to empower the government with newly discovered extractives resources, by helping it to grapple with the complex chain of policy decisions that will be key to transforming new resources into stronger human development outcomes – ranging from public sector spending allocations to leveraging industry spending. Such findings are timely since President Jakaya Kikwete recently took major step towards ensuring fiscal and economic stability by signing legislation that will help ensure revenue from natural gas discoveries bring socioeconomic progress for citizens.
These recent gas discoveries have the potential to bring in as much as 1.4 billion Dollars per year to Tanzania — more than 10 per cent of current government revenues–within the next decade.
The new revenues could help provide basic needs for citizens such as improved primary healthcare and access to quality education. The next step for the government will be to develop detailed regulations and procedures to implement the new laws.
The new administration will face policy decisions on how to manage and allocate resources in a responsible way and in accordance with the laws. Maintaining a focus on human development goals, transparency and ensuring public awareness and debate with key stakeholders and citizens will be crucial.
A new study by the African Development Bank and the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation shows that despite recent drops in commodity prices, revenues from recently discovered oil, gas, and mineral reserves in countries such as Ghana, Liberia, Mozambique, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, and Uganda could add between 9 per cent and 31 per cent to those governments’ revenues. The report, which was launched in Dar es Salaam in early September.
Provides updated projections on the timing and magnitude of these natural resource revenues and guidance on how to effectively direct them toward strengthening health, education, and other social services. Supporting long-term economic growth. In Ghana, for example an estimated one-third of the country’s combined health and education needs over the next decade could be funded from recent oil discoveries.
In Liberia, Mozambique, and Sierra Leone, revenues from recent natural resource discoveries could meet half of health funding needs. The potential opportunities in Tanzania and Uganda are also significant. In this context, African leaders have a valuable opportunity to work with the private sector and civil society to develop long-term plans that link new natural resource revenues with human development goals.
Such plans should be anchored in realistic expectations about the timing and magnitude of new revenues and avoid borrowing against future earnings–a tactic that could easily backfire due to the volatility of oil and gas prices.
At the same time, African countries need to devote resources to prepare for the global transition from fossil fuels to fight climate change. This process is of particular urgency for Sub-Saharan Africa, a region that combines large reserves of oil and gas with a high risk of suffering from large-scale disruptions in temperature and rainfall. The release of the AfDB- Gates Foundation report and the signing of the new legislation in Tanzania have come at a pivotal moment.
In September, global leaders from nearly 200 countries will meet at the United Nations in New York to adopt the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). A central issue for this 15- year global anti-poverty and development agenda is how African countries will help provide the financing needed to meet the basic needs of their people. New natural resource revenues could be a meaningful source of this funding–if they are effectively and responsibly managed.
History is replete with examples of countries that have squandered their natural resource wealth through mismanagement of revenues, inability to harness privatesector investment, and other grave missteps, including human rights violations and environmental degradation.
But some countries–such as Indonesia (with oil) and Chile and Botswana (with mining)–have successfully applied these revenues to stimulate job creation, economic diversification, and expand social services. When policymakers, donors, technical partners, and private companies work together to develop the necessary policies and support smart planning and rigorous management, entire nations can benefit from expanded opportunity and growth.
Tanzania has achieved a commendable milestone but there is more to be done. Through good management principles, we hope that the new legislation will turn into a legacy of good natural resource management that can be followed by other African countries in the months and years to come.









Comments are closed.